Protecting your horse’s health goes beyond daily care—it’s about safeguarding them from invisible threats. What vaccines do horses need to stay safe from potentially life-threatening diseases? Core vaccines like tetanus, rabies, and West Nile virus are non-negotiable, shielding your horse against infections that can cause severe illness or death.
Beyond these, risk-based vaccines, such as those for equine influenza or strangles, are equally vital depending on your horse’s lifestyle, environment, and exposure risk.
Skipping vaccinations isn’t just risky—it can leave your horse vulnerable to painful and preventable conditions. Vaccines not only protect your horse but also curb the spread of diseases within the equine community.
Whether you’re caring for a retired companion or a high-performance athlete, a tailored vaccination plan is essential. Dive into this guide to learn which vaccines are must-haves, when to administer them, and how they contribute to your horse’s long-term health.
Essential Horse Vaccinations
Understanding which vaccines are essential for horses is crucial for maintaining their health and well-being. This section provides an overview of core vaccines and distinguishes between core and risk-based vaccines.
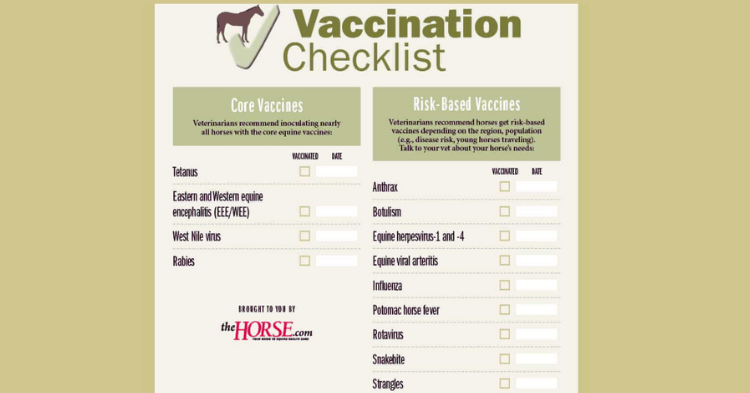
Core Vaccines Overview
Core vaccines are vital for protecting horses against diseases that are prevalent, highly contagious, or pose significant health risks. These vaccines are recommended for all equids, ensuring they receive maximum protection with minimal risk. Core vaccines should be administered annually or semi-annually for best efficacy.
| Core Vaccines | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Rabies | Annually |
| EEE/WEE (Eastern and Western Equine Encephalitis) | Annually/Semi-annually |
| Tetanus | Annually |
| West Nile Virus | Annually/Semi-annually |
(American Association of Equine Practitioners)
Understanding Core Vs. Risk-Based Vaccines
Core vaccines provide broad, essential protection for every horse. They include vaccinations against diseases that are endemic to a region, highly contagious, and/or pose a severe health risk. These vaccines are also important for public health and meet legal requirements in some areas (American Association of Equine Practitioners).
Risk-based vaccines, on the other hand, are tailored to individual horses based on their specific needs and circumstances. These vaccines are recommended by veterinarians considering factors like the horse’s geographic location, lifestyle, travel frequency, and breeding status. Not all horses require risk-based vaccines, and their necessity is assessed on a case-by-case basis (Penn State Extension).
Consultation with a veterinarian is vital to developing a personalized vaccination plan for each horse. Factors like travel, geographic location, and breeding status influence the need for additional, non-core vaccines. Following guidelines from authorities like the American Association of Equine Practitioners (AAEP) ensures that your horse receives the most appropriate and effective protection.
Core Equine Vaccines
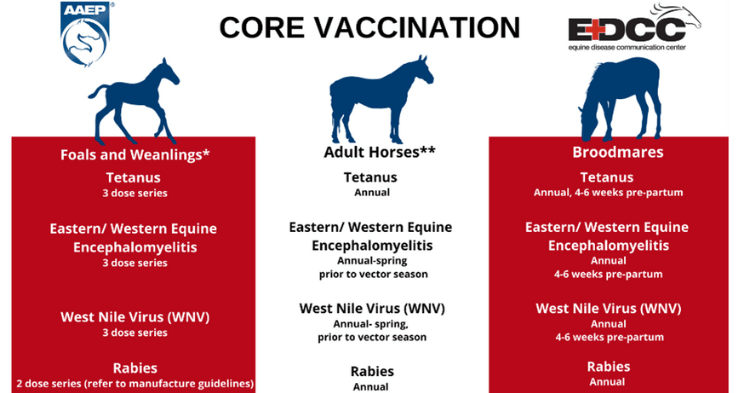
For horse owners, understanding the importance of core equine vaccines is essential for maintaining the health and safety of their animals. Vaccinations against diseases like rabies, tetanus, and encephalitis are fundamental.
Rabies Protection
Rabies is a deadly viral disease that affects the nervous system of mammals, including horses. The rabies vaccine for horses is listed as a core vaccine by the American Association of Equine Practitioners (AAEP) (Penn State Extension). Equine rabies is life-threatening and incurable, making vaccination crucial. The vaccine has been proven to be highly effective, offering a lifetime of protection with one or two shots.
| Disease | Fatality Rate (%) | Vaccination Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Rabies | 100 | Annually |
For more on why these vaccinations are essential, you can read about disease prevention.
Tetanus Prevention
Tetanus is another critical disease that horse owners need to guard against. Known for its often fatal consequences, tetanus, or lockjaw, is caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. Horses are particularly susceptible due to their environment, which often exposes them to the spores from contaminated soil or wounds. The tetanus toxoid vaccine is a core part of a horse’s vaccination regimen.
Vaccination should be administered annually to ensure maximum efficacy (Penn State Extension).
| Disease | Prevention Method | Recommended Vaccination Schedule |
|---|---|---|
| Tetanus | Tetanus toxoid vaccine | Annually |
Encephalitis Vaccination
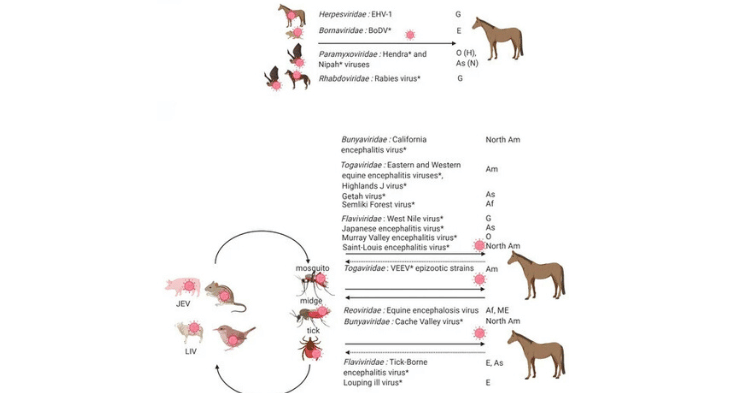
Encephalitis, encompassing diseases such as Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE), Western Equine Encephalitis (WEE), and West Nile Virus, poses a significant threat to horses. These diseases are transmitted primarily by mosquitoes and can result in severe neurological symptoms and high fatality rates.
Vaccination against EEE/WEE and West Nile Virus is crucial, especially in regions where mosquito activity is high. These vaccines are core and should be administered annually to all horses (Penn State Extension). Spring is an optimal time for these vaccinations due to the reemergence of mosquitoes as temperatures rise.
| Disease | Transmission Mode | Recommended Vaccination Schedule |
|---|---|---|
| EEE/WEE | Mosquitoes | Annually |
| West Nile Virus | Mosquitoes | Annually |
For more detailed guidance, visit our section on customizing vaccination plans.
These core vaccines play a critical role in safeguarding horses against severe and often fatal diseases. For any questions about what vaccines do horses need, consult with your veterinarian to develop a tailored vaccination plan that meets the unique needs of your equine companion.
Importance of Core Vaccines
Understanding the importance of core vaccines for horses ensures the well-being of your equine friends and the broader community. These essential vaccinations play a crucial role in both disease prevention and public health significance.
Disease Prevention
Core vaccines for horses are indispensable for safeguarding them against severe and potentially fatal diseases. The American Association of Equine Practitioners (AAEP) identifies core vaccines that are essential for all horses, regardless of their location or lifestyle. These include vaccines for rabies, Eastern and Western Equine Encephalitis (EEE/WEE), tetanus, and West Nile Virus.
Disease Coverage
| Disease | Vaccination Frequency |
|---|---|
| Rabies | Annually |
| Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) | Annually |
| Western Equine Encephalitis (WEE) | Annually |
| Tetanus | Annually |
| West Nile Virus | Annually |
Vaccinating against these diseases is not optional; it is a necessity. Rabies is life-threatening and incurable, but the vaccine has proven to be extremely effective in most horses, offering a lifetime of protection with one or two shots. Regular administration of these vaccines creates a robust immunity shield, preventing outbreaks and ensuring the health of your horse.
Public Health Significance
Beyond the direct benefits to individual horses, core vaccines have significant public health implications. Diseases like rabies and West Nile Virus can also affect humans, making vaccination a critical component in preventing zoonotic disease transmission. The core vaccines are recommended by the AAEP precisely because they address diseases that are either endemic, highly contagious, pose severe health risks, or are legally mandated (AAEP).
It’s fundamental for horse owners to collaborate with veterinarians in creating a comprehensive vaccination schedule. This proactive approach is vital not just for the health of individual horses but for the safety and well-being of the broader community as well. For more detailed information on horse care, explore our article on how long horses live.
By ensuring that horses receive their core vaccines, owners can protect their beloved animals from debilitating diseases and support overall public health. A well-rounded vaccination strategy is a cornerstone of responsible horse ownership and contributes to the long-term health and happiness of horses everywhere. For a deeper understanding of horse care essentials, visit our guide on how to harness horse.
Customizing Vaccination Plans
Consultation with Veterinarian
When considering what vaccines do horses need, it is essential to consult with a veterinarian. A licensed vet can perform a risk assessment that considers various factors such as geographic location, travel, breeding status, and other individual needs of the horse. This approach ensures that the most appropriate and necessary vaccines are administered without incurring unnecessary expenses or risks.
| Factors to Consider | Examples |
|---|---|
| Geographic Location | Diseases prevalent in the region |
| Travel | Exposure risk during events or transport |
| Breeding Status | Additional vaccines for broodmares |
For more detailed guidelines, visit American Association of Equine Practitioners (AAEP).
Personalized Vaccine Protocols
Tailoring a personalized vaccine plan involves selecting both core and risk-based vaccines. Core vaccines are essential for all horses, while risk-based vaccines are advised based on the individual horse’s exposure risk and geographic factors. According to Penn State Extension, not all horses require every available vaccine, making personalization crucial for effective and economical disease prevention.
| Vaccine Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Core Vaccines | Rabies, Tetanus, Encephalitis |
| Risk-Based Vaccines | West Nile Virus, Rhinopneumonitis, Potomac Horse Fever, Strangles |
Risk-based vaccination protocols should be considered for diseases like West Nile Virus and Strangles, which may vary regionally based on likely exposure and disease severity. For protection against these diseases, adherence to AAEP guidelines is recommended for adult horses, broodmares, foals, and previously unvaccinated horses (Penn State Extension).
For more information on horse care and related topics, you can check our articles on what horse won the belmont stakes, why do horses yawn, or how high can horse jump.
Timing and Considerations
Timing and other considerations are crucial when determining what vaccines do horses need. Ensuring vaccinations are administered at the optimal time can significantly improve their effectiveness and the overall health of the horse.
Seasonal Vaccination Factors
Certain vaccines are more critical during specific seasons due to the prevalence of particular diseases. Mosquito-borne diseases like West Nile Virus and EEE/WEE (Eastern and Western Equine Encephalitis) become a heightened risk as insects reemerge with warming weather. Thus, spring is an important time to vaccinate horses against these diseases. Proper timing ensures that horses build immunity before peak mosquito activity.
| Disease | Key Vaccination Time |
|---|---|
| West Nile Virus | Spring |
| EEE/WEE | Spring |
Vaccinating horses prior to the start of “mosquito season” is essential to safeguard them from ailments transmitted by these insects. For additional tips on keeping your horse safe, check out our guide on how horse racing works.
Travel and Public Exposure Risks
When horses travel or are taken to public places, they are exposed to a higher risk of contracting diseases. Risk-based vaccines should be considered, especially if horses are frequently at showgrounds or barns with high horse traffic. Diseases like strangles, equine influenza, and equine herpesvirus (EHV) spread easily in such environments (Penn State Extension).
| Disease | Vaccination Time for Travel/ Public Exposure |
|---|---|
| Strangles | Before travel or public events |
| Equine Influenza | Before travel or public events |
| Equine Herpesvirus (EHV) | Before travel or public events |
For horses that will be shown or travel off the farm, additional risk-based vaccines are recommended. These preventive measures help in avoiding the spread of respiratory diseases easily transmitted from horse to horse. For further information on preparing your horse, refer to our article on what horse has won the triple crown.
Check out more information on:
- how horses are measured
- how long horses live
- why cant horses vomit
- what horses eat
- why do horses eat hay
- why do horses yawn
- how to harness horse
This comprehensive approach to horse vaccinations helps to ensure their safety, health, and longevity, giving horse owners peace of mind and confidence in the well-being of their equine companions.
By considering both seasonal and travel-related factors, horse owners can better protect their companions from various diseases. Always consult a veterinarian to determine the most appropriate vaccination schedule for your horse. For more details on customizing vaccination plans, visit our section on personalized vaccine protocols.