Struggling to figure out how to harness horse properly? You’re not alone. Many horse enthusiasts find themselves frustrated, grappling with unruly straps and confused equines, feeling like every attempt ends in chaos. The challenge can seem daunting—what if your horse becomes skittish or the harness isn’t secure enough? It’s a delicate process, and getting it wrong can put both you and your horse at risk.
But what if mastering this essential skill could transform your equestrian experience? Picture a serene bond between you and your horse, where the harnessing process becomes second nature, setting the stage for smooth rides and meaningful connection.
That’s exactly what this step-by-step guide delivers. Whether you’re a novice rider or looking to refine your skills, you’ll discover techniques that make harnessing straightforward, efficient, and stress-free. Let’s dive into the world of precision and poise, where every detail counts.
Harnessing Your Horse
Harnessing a horse can seem daunting, but understanding the basics and different types of harnesses can make the process smooth and efficient.
Basics of Horse Harnessing
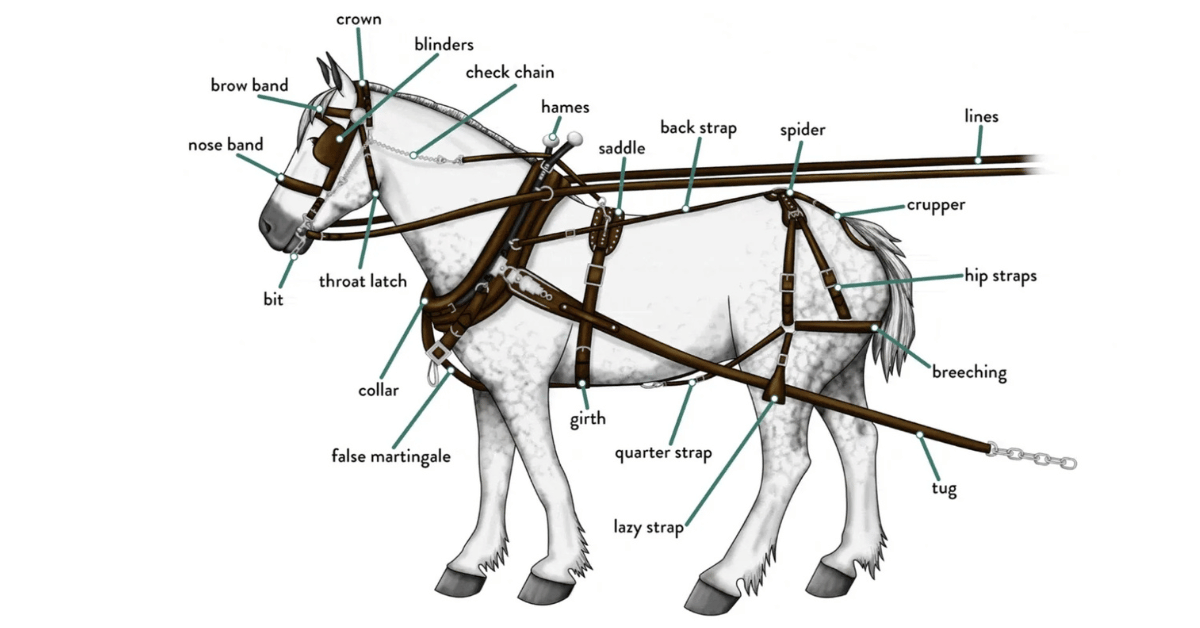
Harnessing a horse involves several steps to ensure that the horse is safely and comfortably prepared to pull a carriage or perform work. Here’s a basic guide on how to harness a horse:
Collar or Breast Strap: Start by putting a collar around the horse’s head if it’s pulling a heavy carriage, or skip the collar and put a breast strap around the horse’s chest if the carriage is fairly light (wikiHow).
Traces: Buckle the traces to the collar or breast strap on both sides of the horse’s body. Traces are the straps that connect the horse to the vehicle it will be pulling.
Saddle: Place the saddle on the horse’s back. This part of the harness helps distribute the weight of the carriage evenly.
Crupper: Secure the crupper around the tail. The crupper prevents the harness from slipping forward.
Bridle and Reins: Finally, place the bridle over the horse’s head and connect the reins. The bridle contains the bit, which goes into the horse’s mouth and allows for steering and control.
Types of Horse Harnesses
Understanding the different types of harnesses is crucial for selecting the right one for your specific needs. Here are the main types:
| Type of Harness | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Work Harness | Made from durable materials like leather and designed for heavy pulling and draft work. | Farm work and carriage pulling. |
| Driving Harness | Typically lighter and used for smaller carts and pleasure driving. Can be made from materials like bio, nylon, and beta. | Recreational driving and light hauling. |
| Show Harness | Often more decorative and designed for show purposes. | Parades, shows, and competitions. |
Horse harnesses can also be customized with various materials for different preferences and needs (My Draft Horse). Accessories like bits, collar pads, and fly protection are also important to consider for enhancing the harnessing experience.
To dig deeper into understanding how fast a horse can run, how fast horse can run, or learn about other horse-related topics, check out more of our articles. By understanding these basics and harness types, horse owners can ensure their horse is properly equipped for any task.
Essential Components

Harnessing a horse involves several critical components, each serving a specific function to ensure both the horse’s comfort and the effectiveness of the harness. Here we will delve into two key components: collars and breast straps, and traces and saddle.
Collars and Breast Straps
- Collars Straps
Used for heavy loads.
Designed to fit around the horse’s neck.
Distributes the pressure evenly across the horse’s shoulders.
Breast Strap
Suitable for lighter loads.
Positioned around the horse’s chest.
| Type of Harness | Usage | Placement | Load Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horse Collar | Heavy loads | Around neck | High |
| Breast Strap | Light to moderate loads | Around chest | Moderate |
For further details on these components, you can explore various harness types available for different horse breeds on websites like My Draft Horse.
Traces and Saddle
The traces and saddle are pivotal for connecting the horse to the carriage and distributing the pulling force.
Traces
Straps that connect the collar or breast strap to the carriage.
Must be durable and appropriately sized.
Buckled tightly to ensure efficient transmission of force.
Saddle (Harness Saddle)
Located on the horse’s back.
Helps to keep the harness in place.
Provides additional support to the traces.
When fastening the crupper around the tail, make sure it is comfortable for the horse to prevent chafing. This secures the back end of the harness, ensuring stability.
For a comprehensive guide on how all these parts come together, a step-by-step approach can be found on websites like wikiHow.
By understanding and properly utilizing these essential components, horseback riders can ensure both the comfort and efficiency of their horses. For more insights into other aspects of horse management, consider reading up on how high can horse jump and what vaccines do horses need.
Getting Started with Harnessing
Harnessing a horse is a crucial skill for every rider or horse owner. Proper harnessing ensures the safety of both the horse and the handler. In this section, we will cover the fundamental steps of placing the bridle and reins, and securing the crupper.
Placing the Bridle and Reins
Placing the bridle and reins on your horse is a critical part of the harnessing process. The bridle is a key piece of equipment that allows you to steer and control the horse.
- Approach Calmly: Always approach your horse quietly and calmly.
- Hold the Bridle Correctly: Hold the bridle by the crown piece, with the bit in one hand.
- Place the Bit: Gently open the horse’s mouth and place the bit inside. The bit should sit comfortably in the horse’s mouth without causing any discomfort.
- Pull the Bridle Over: Pull the bridle over the horse’s ears, ensuring that the browband is sitting flat across the horse’s forehead.
- Secure the Reins: Attach the reins by connecting them to the bit rings. Ensure the reins are not twisted and are of equal length.
For visual guidance and detailed steps, you can refer to this wikiHow guide on harnessing a horse.
Securing the Crupper
The crupper is a strap that loops under the horse’s tail and attaches to the back of the harness. It prevents the harness from slipping forward, providing a secure fit.
- Locate the Crupper: Identify the crupper on the harness. It is usually connected to the back of the saddle.
- Lift the Tail: Gently lift the horse’s tail and place the crupper underneath.
- Adjust the Strap: Ensure that the crupper strap is snug but not tight. It should sit comfortably under the tail without causing chafing or irritation.
- Check the Fit: Check the overall fit of the harness to ensure there is no excessive movement. The crupper should hold the harness in place securely.
For further details and illustrations, the My Draft Horse guide provides excellent resources on harnessing for work-related activities.
Properly placing the bridle and reins, and securely fitting the crupper are essential steps in harnessing your horse. For more insights on harness components, check out our sections on the types of horse harnesses and collars and breast straps.
By understanding and following these steps, you ensure that your horse is safely and comfortably harnessed, paving the way for effective and enjoyable riding experiences.
Tips for Effective Harnessing
Harnessing your horse correctly is essential for both safety and performance. In this section, we will cover tips for the proper use of a full-body harness and the importance of maintenance and inspection.
Proper Use of Full-Body Harness
When it comes to using a full-body harness for your horse, correct usage ensures not only the safety of the horse but also its comfort and performance. Harness components such as collars, breast straps, traces, and saddle need to be securely fastened for optimal function.
- Adjust the Fit: Ensure the harness fits snugly but not too tight. It should be secure enough to stay in place but allow enough room for the horse to breathe and move comfortably.
- Check the Straps: Double-check that all straps are correctly buckled and free of twists. Improperly fastened straps can cause discomfort and reduce the harness’s effectiveness.
- Balanced Load: Distribute the load evenly to prevent undue stress on specific parts of the horse’s body. This helps in minimizing the risk of injury.
- Test Movements: Walk the horse for a few minutes after harnessing to ensure everything is properly placed and comfortable.
Proper harnessing helps in maintaining control and improves overall performance, whether during training or recreational activities. For more insights, visit our section on how fast horse can run.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection of the harness are crucial to ensure its longevity and safety. Poorly maintained equipment can lead to malfunctions and accidents, which can be dangerous for both the horse and the handler.
Maintenance Checklist
- Daily Check: Before and after each use, inspect the harness for signs of wear and tear such as frayed stitching, worn-out straps, and broken buckles.
- Cleaning: Clean the harness regularly to remove dirt and sweat. Use a mild soap and water solution for leather parts, and ensure they are thoroughly dried before storage.
- Lubrication: Apply suitable leather conditioner to keep leather parts supple and prevent cracking.
- Storage: Store the harness in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to avoid damaging UV rays and moisture.
Inspection Checklist
- Monthly Inspection: Conduct a detailed monthly inspection. Look for deeper signs of wear or potential points of failure.
- Repair or Replace: Immediately repair any damaged components or replace them if they are beyond repair to maintain the integrity of the harness.
- Fit Test: Regularly re-test the fit of the harness on your horse. Changes in the horse’s weight or condition could necessitate adjustments in the harness fit.
By adhering to these maintenance and inspection practices, you ensure the safety and effectiveness of your horse’s harness, thereby optimizing performance and comfort. For additional guidance, consider reading our articles on how horses are measured and what horse is bigger than a Clydesdale.
Maintaining a rigorously inspected and well-maintained harness system is essential for safe and effective horse harnessing practices. Ensuring that all components are in top condition not only enhances your horse’s performance but significantly reduces the risk of accidents. For more tips, explore our pages on riding gear selection and safety measures for riding.
Customizations and Safety Tips
Tailored Harness Options
When it comes to harnessing your horse, one size does not fit all. Customizations play a significant role in ensuring comfort and efficiency for both the horse and the handler. Tailored harness options can address specific needs, whether you’re using the horse for riding, driving, or agricultural work.
Types of Customizations
- Padding Adjustments: Extra padding on the breast straps and collars can prevent chafing and distribute pressure evenly.
- Size Variations: Harnesses can be custom-fitted to suit different horse sizes, from ponies to draft horses.
- Material Alternatives: Different materials such as leather, nylon, or biothane can be chosen based on durability and comfort.
Common Customizations Table
| Customization | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Extra Padding | Additional cushioning on key pressure points | Enhanced comfort and reduced chafing |
| Material Choice | Selection between leather, nylon, biothane | Durability and ease of maintenance |
| Size Adjustments | Tailoring to horse’s body measurements | Improved fit and minimized slipping |
To understand more about how specific horse measurements can affect harness fitting, visit how horses are measured.
Training and Hazard Awareness
Proper training and awareness of potential hazards are crucial for safely harnessing and handling horses. These measures will help prevent injuries and ensure a safe environment for both the horse and handler.
Essential Training Tips
- Gradual Introduction: Gradually introduce the horse to the harness to help it become accustomed to the gear.
- Consistent Routine: Maintain a consistent harnessing routine to instill confidence and predictability in the horse.
- Positive Reinforcement: Use treats or gentle patting to reward the horse for standing still during the harnessing process.
Hazards and Safety Precautions
- Proper Use of Full-Body Harness: Ensure that the full-body harness is used correctly and efficiently to reduce the risk of injuries.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of the harness are necessary to ensure peak performance and reliability (FrenchCreek Fall Safety).
- Appropriate Training: Training, and awareness of potential hazards are critical for preventing accidents and promoting a safe environment (FrenchCreek Fall Safety).
By customizing harness options and emphasizing training and hazard awareness, you can ensure a safer and more comfortable experience for both you and your horse. For additional horse riding and safety tips, explore our articles on how fast horse can run and safety measures for riding.
Horse Equipment Essentials
When it comes to horseback riding, having the right equipment is crucial for both safety and comfort. This section will guide you through essential riding gear and safety measures to ensure a positive riding experience.
Riding Gear Selection
Selecting the right riding gear is crucial for safety, performance, and comfort. Here are some of the essential items you need:
- Helmet: A proper horse riding helmet is a must for all equestrians due to the high risk of head trauma. Helmets specifically designed for horseback riding come equipped with advanced safety technology (Farm House Tack).
- Safety Vest: Safety vests protect the torso from impacts in case of a fall. They come in various styles, including some filled with air for enhanced safety (Farm House Tack).
- Riding Pants: Breeches are specially designed riding pants made from thin, stretchy, and chafe-preventing fabric. They often feature gripping fabric to improve communication and maintain stability while riding (Farm House Tack).
- Grooming Tools: Grooming tools help keep horses fit and healthy by aiding in coat shine, circulation, early detection of health issues, and bonding with the horse (Farm House Tack).
Safety Measures for Riding
Every rider must adhere to safety measures to ensure both their own and their horse’s well-being:
- Check Your Equipment: Regularly inspect all riding gear, including the saddle, bridle, and stirrups, for signs of wear and tear. Replace any damaged equipment promptly.
- Use Proper Footwear: Always wear boots with a heel to prevent your foot from slipping through the stirrup. This minimizes the risk of being dragged in case of a fall.
- Apply a Safety Vest: Ensure you’re wearing your safety vest correctly. It provides crucial protection to your torso and ribcage.
- Pre-Ride Warm-Up: Spend some time warming up your horse before riding. This can help relax your horse and reduce the risk of sudden, unpredictable movements.
- Stay Aware: Always be aware of your surroundings and potential hazards. Knowing how fast a horse can run or how high it can jump can help you anticipate and react appropriately during rides.
- Know Your Limits: Don’t attempt maneuvers or ride in conditions that you or your horse are not trained for. Understanding your and your horse’s limits is key to staying safe.
Implementing these safety measures ensures a secure and enjoyable riding experience. For more detailed advice, you can explore articles like how fast a horse can run, how high a horse can jump, and how horse racing works.