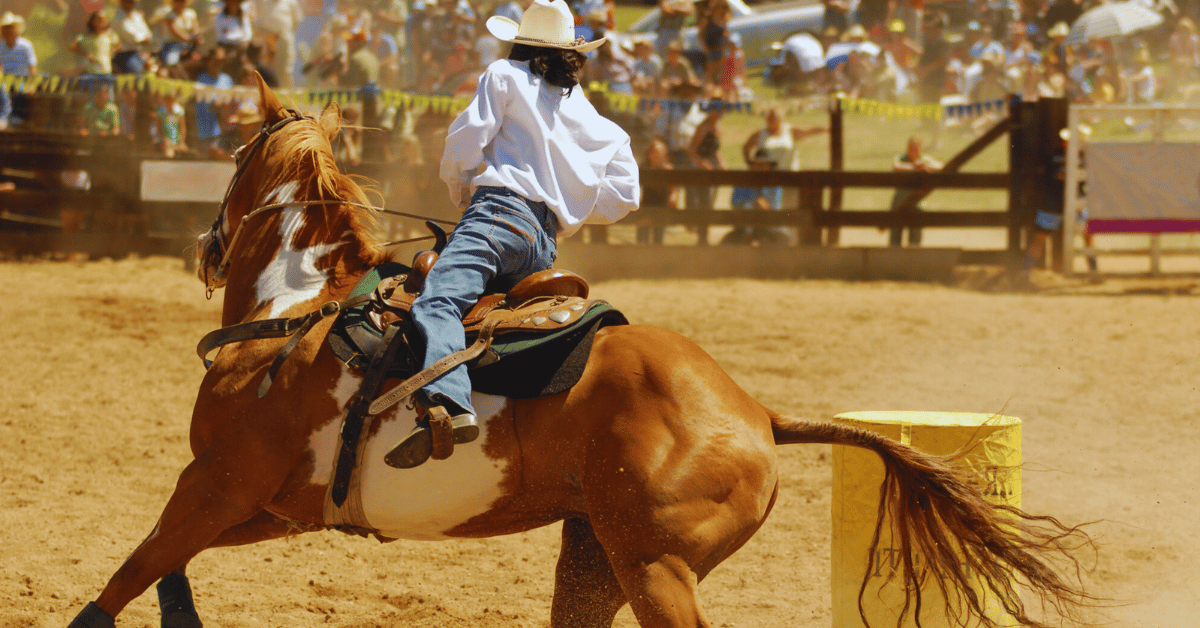
When horses thunder down the track, you might wonder, do horses know they are racing, or are they simply following cues? The answer is complex yet fascinating. Horses possess a natural competitive spirit, honed through centuries of survival in the wild, where speed often meant the difference between life and death.
In a racing environment, this instinct is heightened. Horses recognize the energy of competition—the cheers, the presence of other horses, and the commands of their riders. While they may not grasp the concept of winning in human terms, many horses exhibit behaviors that suggest they understand the need to outpace others. Their focus, drive, and responses indicate an acute awareness of the activity around them.
Ultimately, the key to a fulfilling racing experience lies in ensuring the horse’s physical and emotional well-being. By respecting their instincts and capabilities, we can foster a relationship that celebrates their natural talent and zest for movement.
Understanding Horse Behavior

Sensory Abilities of Horses
Horses possess remarkable sensory abilities that help them thrive as prey animals. Their keen senses enable them to detect subtle changes in their environment and communicate effectively with other horses and humans.
Vision: Horses have an acute ability to detect movement, which is why they can be more flighty on windy days as normally stationary objects are perceived as threats. Using both eyes (binocular vision), their vision is enhanced by about five times.
Hearing: Horses have a keen sense of hearing. They can move their ears 180 degrees, using 10 different muscles for this movement. This ability helps them detect and locate sounds, orienting themselves toward the source of the noise (Rutgers Equine Science Center).
Communication through Body Language
Effective communication is essential for horses, and they primarily use body language to convey their feelings and intentions.
Facial and Body Signals: Horses communicate with humans through body language, using their faces, ears, legs, backs, tails, and entire bodies to convey information. These subtle cues are crucial for their survival.
Signs of Well-being or Discomfort: One of the key ways horses communicate with humans is by displaying signs indicative of their well-being, sickness, or pain. This communication is essential for horse owners to monitor their horse’s health and comfort.
Expressions of Stress: Horses express stress through various behaviors, such as forward-pointing ears, wide-open eyes, widened nostrils, a high head, a stiff stance, a raised tail, defecation, and licking and chewing after a stressful situation (The Horse). Recognizing these signs can help horse owners take appropriate measures to ease their horse’s stress.
Displeasure: Horses clearly express their displeasure through body language, indicating discomfort or unhappiness in response to situations like riding techniques or grooming methods. Understanding these signals enables better handling and care practices.
These communication cues and sensory abilities play a significant role in understanding whether horses know they are racing. Horse owners frequently observe these behaviors and signals to ensure their animals’ well-being, especially during physically demanding activities such as racing. For a deeper understanding of specific horse behaviors, check out the articles on can horses eat apples, do horses get tired of standing, and can horse see in the dark.
Social Dynamics and Well-being
Exploring the social dynamics within horse herds provides essential insights into their behavioral patterns and overall well-being. Understanding their social structures and recognizing signs of stress and discomfort can improve the care provided to these magnificent creatures.
Leadership Hierarchy in Horse Herds
Horses live in herds with a well-defined leadership structure, often led by an older mare known as the alpha mare. Despite the stallion owning the herd, it is the alpha mare who leads due to her experience and ability to navigate threats. The leadership hierarchy ensures that the herd operates smoothly, with the alpha mare guiding movements and making most of the decisions related to safety and foraging.
| Role in Herd | Description |
|---|---|
| Alpha Mare | Dominant mare, leads the herd due to experiences and survival skills |
| Stallion | Owns the herd, but follows the lead of the alpha mare |
| Other Members | Follow the directive of the alpha mare and the stallion |
This structure not only plays a crucial role in the herd’s survival but also in reducing conflicts within the group. Horses rely on this hierarchy for a sense of security, indicating that structured leadership is part of their social makeup.
Signs of Stress and Discomfort
Horses express their stress and discomfort through various behaviors and body language. Recognizing these signs is vital for maintaining their well-being. Vices, or negative activities, can be indicative of underlying stress or boredom. Some of these vices include:
- Cribbing: Biting and sucking on objects, often a coping mechanism.
- Weaving: Repetitive swaying motion from side to side.
- Stall Kicking: Kicking the walls of their enclosure.
- Wood Chewing: Gnawing on wooden structures.
- Self-Mutilation: Biting or harming themselves.
These behaviors can result from conditions such as confinement in stalls, lack of natural stimuli, or nutritional deficiencies.
Additionally, horses communicate their displeasure with humans through subtle body language. Common signs of discomfort include:
| Behavior | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Tail Swishing | Irritation or annoyance |
| Head Shaking | Discomfort, especially with bit pressure |
| Mouth Opening | Response to bit pressure or discomfort |
| Agitation During Grooming | Discomfort or pain (The Horse) |
For horse owners, understanding these signs is crucial for providing appropriate care and addressing any potential issues promptly. Knowing how to interpret a horse’s body language ensures their needs are met, contributing to their overall well-being and comfort.
Relevant internal links:
Cognitive Abilities of Horses
Horses exhibit advanced cognitive abilities that often surprise horse owners. Understanding their emotional perception and problem-solving abilities can offer insight into their daily experiences and interactions.
Emotional Perception in Horses
Horses are capable of distinguishing between positive and negative human facial expressions. Research from 2016 revealed that horses showed increased heart rates when exposed to angry faces and displayed behaviors indicating their perception of human emotions (Horse and Rider). This suggests that horses can read and react to the emotional states of humans, highlighting their sensitivity and emotional depth.
| Human Expression | Horse Reaction |
|---|---|
| Happy | Calm, relaxed |
| Angry | Elevated heart rate, signs of discomfort |
Horses communicate discomfort or unhappiness through body language, such as swishing tails, head shaking, and agitation during grooming (The Horse). Recognizing these signals can help owners better understand their horse’s emotional state and respond appropriately.
For more on how horses interact with their environment, visit do horses like humans.
Problem-Solving and Learning
Horses also demonstrate notable problem-solving skills. In a 2016 experiment at Kobe University, horses used symbols to communicate preferences, associating symbols with actions like “put blanket on” and “take blanket off” (Horse and Rider). This shows that horses can understand and convey complex concepts, indicating advanced cognitive abilities.
Furthermore, another study from 2016 highlighted that horses adjust their signals and interactions based on the awareness of their human caretakers. The horses interacted differently based on whether the caretaker knew the location of a carrot, demonstrating an understanding of others’ states of mind (Horse and Rider).
For more insights into the cognitive abilities of horses, understand how they might relate to questions like do horses know when they are going to die.
| Cognitive Skill | Demonstration | Study |
|---|---|---|
| Communication through symbols | Using icons for actions | Kobe University, 2016 |
| Understanding human awareness | Adjusting signals based on caretakers’ knowledge | Horse and Rider, 2016 |
| Perception of human emotions | Elevated heart rate from angry faces | Horse and Rider, 2016 |
By recognizing and appreciating these cognitive abilities, horse owners can enhance their training and interaction methods. Understanding a horse’s emotional perception and problem-solving skills can lead to a more empathetic and effective approach to equine care.
For more on equine behavior and interaction, explore resources on can horse walk backward and do horses like to race.
Conditioning and Training
Ensuring proper conditioning and training for horses is crucial for their overall health and performance. Below, we delve into the importance of physical conditioning and how to monitor the fitness and health of these majestic animals.
Importance of Physical Conditioning
Conditioning and physical training are essential for horses, significantly enhancing their ability to perform various tasks. Effective conditioning impacts their muscular, skeletal, respiratory, and cardiovascular systems, reducing the risk of injury and related health issues.
Aerobic Conditioning: Enhances the ability of horses to perform all types of exercise. It increases their aerobic capacity, allowing them to perform longer exercise bouts when energy is supplied aerobically. This is particularly important for horses engaged in predominantly anaerobic tasks like those in Quarter Horse and Thoroughbred races.
Skeletal System Improvement: Conditioning aims to fortify the skeletal system, making bones more resistant to stress and improving bone mass and density. However, inappropriate or excessive exercise can lead to issues such as stress fractures, abnormal growth, and bone failure, particularly in young horses.
| Conditioning Focus | Benefits | Risks (if not properly managed) |
|---|---|---|
| Aerobic Conditioning | Increased aerobic capacity, longer performance durations | Overexertion, fatigue |
| Muscular Development | Enhanced strength, stamina | Muscle strain, joint issues |
| Skeletal Fortification | Improved bone density, stress resistance | Stress fractures, growth abnormalities |
Understanding these aspects can help owners and trainers cater to the horse’s individual needs, ensuring optimal performance and well-being.
Monitoring Fitness and Health
Monitoring the fitness and health of a horse during conditioning involves several key indicators. Accurate assessments can reveal critical insights into the horse’s physical condition and response to training.
Heart Rate: An accurate indicator of a horse’s response to exercise, with normal resting heart rates for mature horses ranging from 30 to 40 beats per minute. Different exercise heart rates (below 150-180 beats per minute or above) indicate whether energy is supplied aerobically or anaerobically. Conditioning can help lower heart rates at similar exercise intensity levels.
Respiratory Volumes and Ventilation Rates: Assessing these can provide insights into the horse’s respiratory efficiency and overall fitness levels.
Muscle Function and Stride Movements: Observing muscle responses and stride patterns can indicate improvements or issues in the horse’s muscular system.
Body Condition and Physical Appearance: Changes in body condition, coat quality, and overall appearance are crucial indicators of the horse’s health.
Behavioral Changes: Recognizing small changes in behavior can signal how well the horse is coping with the conditioning regime.
Field Tests: Blood tests, ultrasounds, and X-rays are valuable tools for detecting underlying issues that may not be visible externally.
| Monitoring Aspect | Normal Range/Indicator | What It Reveals |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 30-40 bpm (resting) | Fitness level, response to exercise |
| Respiratory Rates | Variable | Respiratory efficiency |
| Muscle Function | Smooth, fluid movements | Muscle health, strength |
| Body Condition | Smooth coat, healthy weight | Overall health |
| Behavioral Changes | Calm demeanor | Coping ability |
Keeping accurate records and paying close attention to these indicators are crucial for successful conditioning. For further details on horse fitness and health, check out topics like can horse sweat, can horse burp, and do horses get tired of standing.
By understanding the importance of conditioning and monitoring health, horse owners can ensure their companions remain fit, healthy, and ready for any challenge, including knowing if do horses know they are racing and performing optimally during races.
